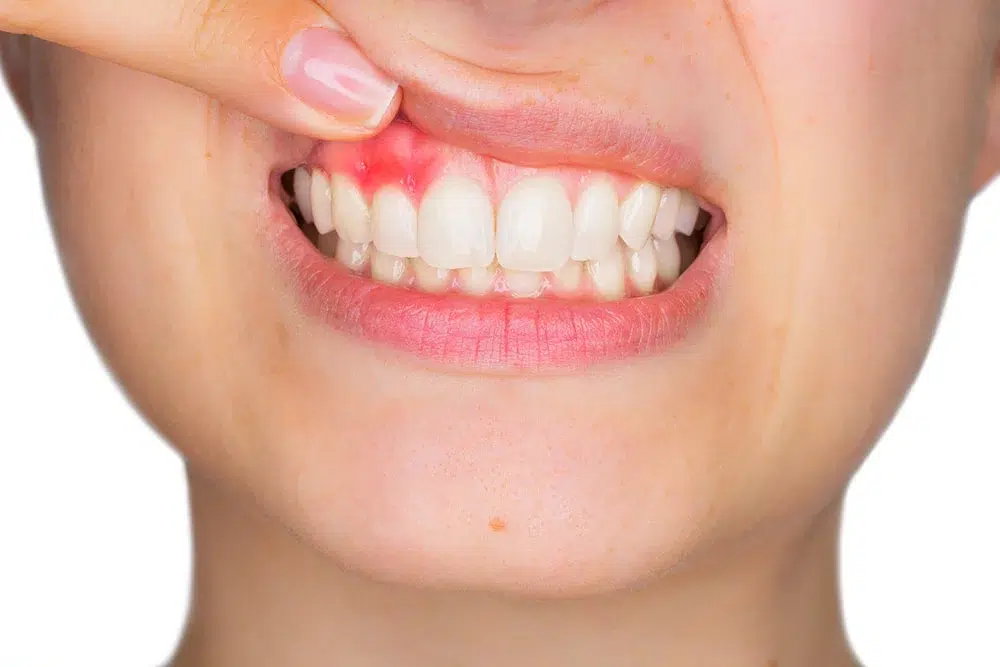
Inflamed gums, also known as gingivitis, are an oral health problem that affects people of all ages. Although they may often seem like a minor annoyance, if not treated in time, they can develop into more serious problems such as periodontitis. In this blog post, we’ll explore the most common causes, symptoms and treatments for inflamed gums, as well as preventive measures you can take.
What are swollen gums?
Inflamed gums are the body’s response to the buildup of bacteria in the mouth, primarily at the gum line. This problem can manifest with redness, swelling, bleeding and, in some cases, pain. Detecting and treating gum inflammation early is essential to prevent the progression of more severe periodontal disease.
Causes of gum inflammation
There are multiple factors that can cause inflammation of the gums, among which the following stand out:
- Bacterial plaque
The main cause of gum inflammation is the accumulation of bacterial plaque. This sticky film forms on the teeth from a combination of food debris and bacteria. If not removed by brushing and flossing, plaque hardens into tartar, which irritates and damages the gums. - Poor oral hygiene
Failure to properly brush or floss teeth with adequate frequency contributes significantly to plaque buildup, which in turn leads to inflammation of the gums. - Hormonal changes
During pregnancy, menstruation or menopause, hormonal changes can increase the sensitivity of the gums, making them more prone to inflammation. - Smoking
Tobacco use not only damages teeth and gums, but also weakens the immune system, making it difficult for the body to fight gum infections. - Nutritional deficiencies
Lack of essential nutrients, such as vitamin C, can affect the health of gingival tissue and increase susceptibility to inflammation. - Medications
Some drugs, such as antihypertensives, immunosuppressants or anticonvulsants, can cause side effects on oral health, including abnormal gum growth or dry mouth, which promotes inflammation. - Systemic diseases
Diseases such as diabetes and HIV/AIDS can weaken the body’s defenses, increasing the risk of developing gum problems.
Symptoms of swollen gums
It is important to recognize the early signs of gum inflammation in order to take immediate action. Some of the most common symptoms include:
- Red or purplish-colored gums: A change in the color of the gums is an indication of inflammation.
- Swelling: Gums appear larger and are tender to the touch.
- Bleeding when brushing or flossing: If your gums bleed easily, they are probably inflamed.
- Pain or tenderness: Gums may feel painful when chewing or touching.
- Receding gums: In some cases, the gums may begin to recede, exposing more of the teeth.
- Bad breath: The accumulation of bacteria due to inflammation can cause halitosis.
Treatments for swollen gums
Treatment for inflamed gums varies depending on the severity of the case. It is essential to address the underlying cause of the inflammation to avoid complications. Treatment options include:
- Improving oral hygiene
The first step in treating inflamed gums is to improve oral hygiene. Brushing teeth at least twice a day, flossing daily and rinsing with an antimicrobial mouthwash can significantly reduce inflammation. - Visit the dentist
It is crucial to see a dentist as soon as you notice symptoms of swollen gums. A dentist will be able to correctly diagnose the cause of the inflammation and recommend appropriate treatment. In addition, a professional cleaning is essential to remove accumulated plaque and tartar that cannot be removed by regular brushing alone. - Professional cleaning
If inflammation is severe or persists despite improved oral hygiene, the dentist may perform a deep cleaning to remove tartar from below the gum line. This procedure, known as scaling and root planing, helps remove bacteria and soften the roots of the teeth, which facilitates healing of the gums. - Mouth antiseptics
Mouthwashes containing chlorhexidine or hydrogen peroxide may be recommended to reduce bacteria in the mouth and relieve gum inflammation. - Antibiotics
In severe cases of gingivitis, the dentist may prescribe antibiotics, either in the form of tablets, gels or rinses, to treat the bacterial infection that is causing the inflammation. - Periodontal surgery
If gingivitis progresses to periodontitis, a more serious gum disease, surgical treatment may be necessary. Periodontal surgery involves periodontal pocket reduction or gum grafting to restore damaged tissue and protect the underlying bone structure.
Prevention of gum inflammation
Prevention is key to maintaining healthy gums. Here are some tips to avoid gum inflammation:
- Proper daily brushing: Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste to brush at least twice a day.
- Flossing: Regular flossing is crucial to remove plaque from the areas between the teeth.
- Balanced diet: Eating a diet rich in fruits and vegetables and low in sugar can improve gum health.
- Avoid smoking: Quitting smoking is one of the best ways to reduce the risk of gum problems.
- Regular dental visits: Visit the dentist at least twice a year for checkups and professional cleanings.
Conclusion
Inflamed gums are a common but treatable problem if detected early. Improving oral hygiene, seeing your dentist regularly and adopting healthy habits are essential to prevent inflammation and prevent it from developing into major complications. If you notice symptoms such as swelling, redness or bleeding, do not hesitate to seek dental care to preserve the health of your gums.
Artículos relacionados
Comprehensive oral health
Comprehensive oral health, Restorative dentistry
Aesthetic dentistry, Comprehensive oral health